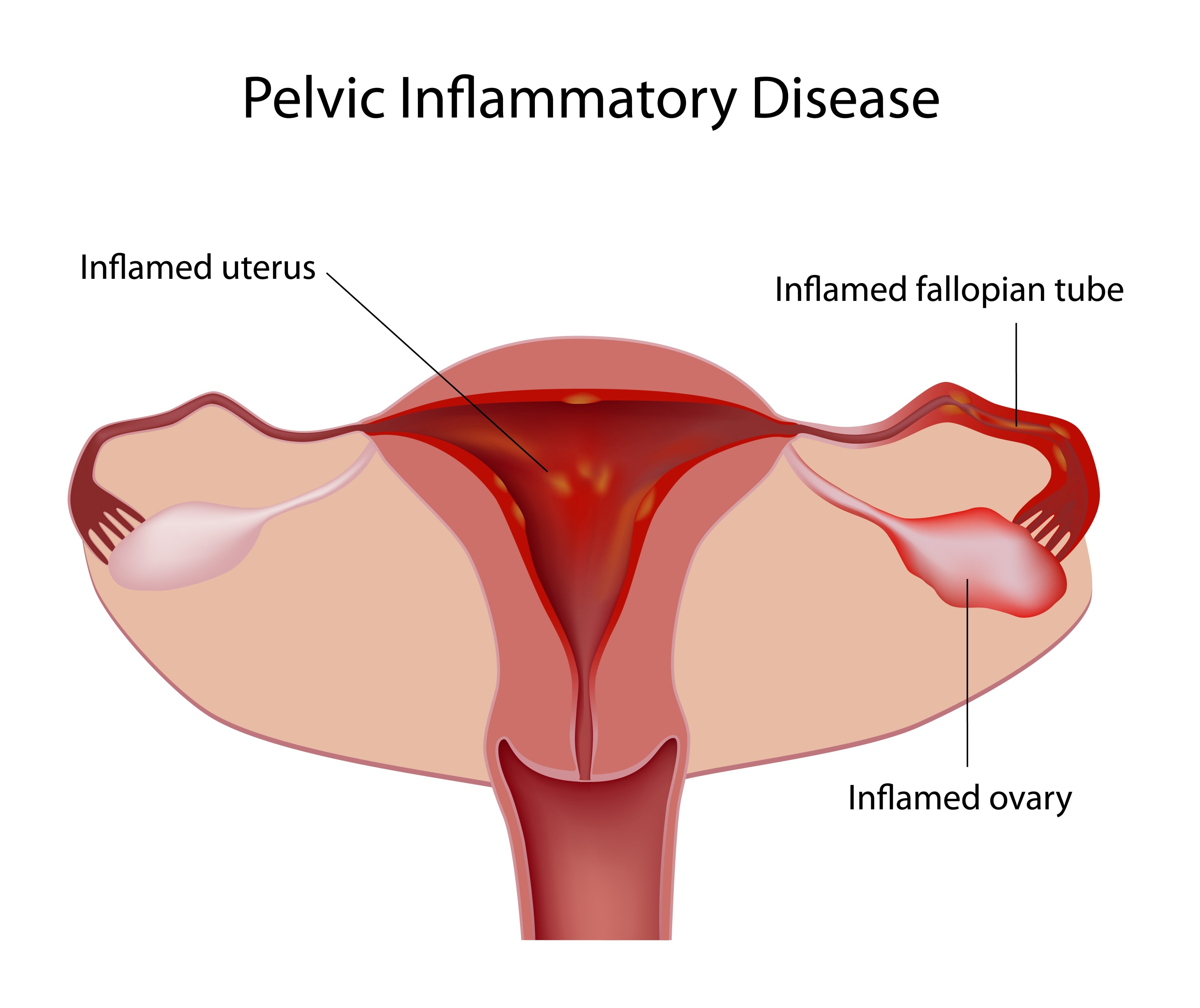
It’s treatable and preventable, yet according to the National Health Institute, 1 million women in the United States get Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) every year – and 1 in 8 of those women will suffer from infertility as a result. PID is a contagious and common infection in a woman’s reproductive organs, most often the result of a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI). A serious complication of some STIs, PID occurs when certain bacteria – most commonly, chlamydia or gonorrhea – travel upward from a woman’s vagina or cervix into her womb, fallopian tubes, or ovaries. Other infections that are not sexually transmitted can also cause PID; in fact, normal bacteria found in the vagina and on the cervix can sometimes cause PID, but no one is sure why this happens.
About 1 in 8 sexually active girls will have PID before age 20, yet many women who develop it will either experience no symptoms or won’t seek treatment. PID may be detected only later, when you have trouble getting pregnant or if you develop chronic pelvic pain.